Electricity is a fundamental part of our modern lives, powering everything from the devices in our homes to the industries that drive economies. While we often take it for granted, understanding how electricity is generated is a fascinating journey into the heart of one of humankind's most transformative inventions—the generator.
The Basics of Electricity Generation
Electricity generation is a process that converts various forms of energy into electrical power. The heart of this process is the generator, a device that harnesses mechanical energy and turns it into electrical energy. Here's a simplified breakdown of how generator parts work together to create energy:
Most generators are powered by some form of mechanical energy. This can be obtained from various sources, including steam, water, wind, or an engine's combustion of fossil fuels. The mechanical energy source sets a conductor (usually copper or aluminum wire) in motion to generate electricity. This conductor is often in the form of a coiled wire, which is spun within a magnetic field.
When the conductor moves within the magnetic field, it induces an electrical current within the wire due to the principles of electromagnetic induction. This current flows through the wire and becomes the generator's electrical output. The electrical current produced can be harnessed and used for various applications, from lighting up your home to powering complex machinery.
What Are Generators Used For?
Generators are versatile devices used for various applications where a reliable electrical power source is needed. They provide electricity when the grid is unavailable, during power outages, or in remote locations. Some of the most common uses for generators are:
Emergency and Residential Power Backup: Homeowners use generators to keep essential appliances and systems running during power outages. This includes providing electricity for refrigeration, heating and cooling, lighting, and electronic devices.
Generators are also commonly used to provide backup power during electrical grid outages and for disaster relief. They ensure that critical systems, such as hospitals, data centers, and emergency services, continue to operate without interruption.
Industrial and Commercial Applications: Generators are essential for industries and businesses to maintain continuous operations, especially during planned outages.
 They are used to power machinery, manufacturing processes, data centers, and other critical systems. Generators also provide:
They are used to power machinery, manufacturing processes, data centers, and other critical systems. Generators also provide:
- On-site power for construction projects
- Enabling the operation of tools
- Equipment
- Temporary lighting and heating
Outdoor Events, Festivals, and Remote Locations: Generators supply power for outdoor events, concerts, festivals, and fairs, ensuring lighting, sound systems, food preparation, and other amenities can function smoothly. In areas without access to a reliable electrical grid, such as remote construction sites, cabins, and wilderness locations, generators are used to supply power for lighting, appliances, and tools.
Recreational Activities and Agriculture: Generators power equipment and appliances for recreational activities, including camping, RV travel, boating, and tailgating. Generators are also used in farming for irrigation systems, powering farm equipment, and providing electricity to barns and storage facilities.
Telecommunications and Healthcare: Telecommunication towers and networks often rely on generators for backup power to maintain communication services during grid failures or natural disasters. Hospitals and healthcare facilities use generators to ensure uninterrupted power for medical equipment, patient care, and critical life support systems.
What Are the 3 Main Types of Generators?
Generators come in various forms and are classified based on their energy sources and operational principles. The three main types of generators are internal combustion engine generators, turbine generators, and solar generators.
1. What Are Internal Combustion Engine Generators?
Internal combustion engine generators are commonly used in portable and standby generators. They rely on the combustion of fuels like gasoline, diesel, or natural gas to turn an internal combustion engine, which drives the generator. They are often found in home standby generators, construction sites, and mobile power sources.
Diesel generators are a subset of internal combustion engine generators that specifically use diesel fuel for power. They are known for their durability and efficiency, making them a common choice for backup power in various applications.
2. What Are Turbine Generators?
Turbine generators are often found in large power plants. The kinetic energy of moving fluids, such as steam, water, or gas, powers them. These generators convert the mechanical energy generated by the turbine into electrical energy. Examples include steam turbines, wind, hydroelectric power, and gas turbine generators.
Wind turbines use the wind's kinetic energy to spin their blades. The rotational energy generated is then used to rotate a generator, producing electricity. Wind turbine generators are a vital component of wind power systems and are used for renewable energy generation.
Hydroelectric power plants utilize the force of falling or flowing water to turn a generator. The potential energy of the water is converted into electrical energy as it falls through turbines. Hydroelectric generators are a significant source of renewable electricity.
3. What Are Solar Generators?
Solar generators, often referred to as solar panels, capture energy from sunlight using photovoltaic cells. These cells convert solar energy into electricity. Solar generators are used for renewable energy generation in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
What Are the Different Generator Parts?
 Generators are complex machines with numerous components that work together to generate electrical power. Although there are several different varieties, you can typically find several common generator parts in every piece of equipment:
Generators are complex machines with numerous components that work together to generate electrical power. Although there are several different varieties, you can typically find several common generator parts in every piece of equipment:
- Engine: The engine is the primary generator part that provides the mechanical energy needed to drive the generator. It can be an internal combustion engine (diesel, gasoline, natural gas) or a turbine (steam, gas, or water), depending on the generator type.
- Alternator or Generator Head: This is the core generator part that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It includes a rotor (armature) and a stator with wire coils. The rotor is attached to the engine and rotates within the stator to induce electrical current.
- Fuel System: For internal combustion engines, the fuel system includes generator parts like the fuel tank, fuel lines, fuel pump, and injectors or carburetor, depending on the engine type. It provides the necessary fuel for engine operation.
- Cooling System: Generators often have cooling systems to regulate the engine's temperature. This collection of generator parts typically includes a radiator (for liquid-cooled engines), a fan, and cooling fluid (coolant). Air-cooled generators rely on fans and fins for cooling.
- Exhaust System: The exhaust system consists of two main generator parts: an exhaust manifold and a muffler. It manages and directs the engine's exhaust gases away from the generator.
- Voltage Regulator: The voltage regulator ensures that the electrical output from the generator is stable and within a specified voltage range. It prevents voltage spikes or drops that can damage connected electrical equipment.
- Governor: The governor is the generator part that controls the engine's speed, maintaining it at a consistent level to regulate the frequency (Hertz) of the generated electricity. This is crucial for stable power output.
- Generator Control Board: The generator control board provides user interface and monitoring functions. It includes features like start/stop controls, output voltage and frequency displays, circuit breakers, and safety indicators.
- Battery: In some generators, a battery is used to initiate the engine's starting process. It's commonly found in standby generators to ensure they can start automatically during power outages. A battery that won’t charge may be due to a faulty battery charger. Thankfully, these generator parts are easy to test and replace if necessary.
- Filters: Clean air and pure fuel and oil are essential for efficient engine operation. A generator air filter prevents dust and debris from entering the engine's combustion chamber, while the fuel filter removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel supply to ensure clean and reliable fuel for the engine. To keep these generator parts working seamlessly, an oil filter removes particles and contaminants from the engine's lubricating oil.
- Circuit Breaker: The circuit breaker is a generator part that protects the engine from overloads and short circuits by interrupting the electrical circuit if an issue is detected.
- These generator parts work together to produce electricity reliably, whether it's for backup power during outages, supplying electricity in remote locations, or serving as a primary source of electrical power in various settings. In addition to primary components, there are three optional inclusions that you may also find on your generator.
- Optional Generator Parts:
- Coolant Heater: For cold climates, generators may be equipped with a coolant heater to ensure the engine starts and operates in low temperatures. You can also purchase cold weather kits to keep your generator safe in the winter months.
- Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): Standby generators often include an ATS, which detects a power outage and automatically switches the electrical load from the utility grid to the generator.
- Soundproof Enclosure: Generators can be enclosed within soundproof housing to reduce noise and ensure quiet operation.
9 Ways to Improve the Lifespan of Your Generator
Generator maintenance is essential to ensure the reliable and efficient operation of your generator. Remember to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for maintenance schedules and procedures specific to your generator model. From keeping it in a safe location to ensuring all generator maintenance and repairs are addressed in a timely fashion, there are several quick and easy ways to extend the life of your generator, including:
1. Regular Inspections
Perform routine visual inspections to check for signs of wear, damage, leaks, or loose components. Inspect all of the generator parts, including the engine, alternator, fuel system, exhaust system, and electrical connections. Don't forget to check the exhaust system for any leaks, damage, or obstructions. A healthy exhaust system ensures proper gas evacuation, which not only prolongs the life of your generator but also helps reduce environmental impact by using fuel more efficiently.
2. Routine Generator Maintenance
There are several systems that need routine generator maintenance, as well as generator parts that need to be replaced regularly. These are:
- Fuel system
- Oil changes and filters
- Generator air filter and cooling system maintenance
- Battery maintenance
- Fuse repair and replacement
- How to Perform Routine Generator Maintenance
 Inspect and clean the fuel system components, including the fuel tank, lines, filters, and injectors or carburetors. Ensure the fuel is clean and free from contaminants. If the generator is not used frequently, use fuel stabilizers to prevent fuel degradation and varnish buildup in the fuel system.
Inspect and clean the fuel system components, including the fuel tank, lines, filters, and injectors or carburetors. Ensure the fuel is clean and free from contaminants. If the generator is not used frequently, use fuel stabilizers to prevent fuel degradation and varnish buildup in the fuel system.
Regularly change the engine oil according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Proper lubrication is crucial for the engine's longevity and performance. Replace the oil filter during generator maintenance when changing the engine oil. A new filter helps maintain clean oil for engine lubrication.
Clean or replace the generator air filter at the recommended intervals. A clean generator air filter ensures the engine receives clean air, leading to efficient combustion. Maintaining the cooling system, checking the coolant level, inspecting hoses and connections, and cleaning the radiator or cooling fins. Overheating can damage the engine.
If your generator has a battery, regularly check its charge level, terminals, and connections. Keep it charged to ensure reliable starting.
Generator fuses are typically rated for specific amperages, and they should be carefully selected to match the load and the electrical system's requirements. Regular inspection and testing of these generator parts are important to ensure that they are in good working condition. If a fuse blows, it should be replaced with the correct amperage-rated generator fuse to maintain the safety and functionality of the generator's electrical circuits.
3. Load Testing
Periodically conduct load testing to ensure your generator can handle its maximum capacity. This verifies its readiness for emergencies.
4. Testing Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS)
For standby generators, test the ATS to ensure it functions correctly. These generator parts should switch between utility power and generator power seamlessly during tests.
5. Voltage and Frequency Checks
A multimeter measures the generator's voltage and frequency output. Ensure they are within the specified range for safe and reliable operation.
6. Exercise the Generator
Run the generator at least once a month, allowing it to operate under load for a brief period. This keeps the engine and components lubricated and helps identify potential issues.
7. Keep a Maintenance Log
Maintain a detailed log of all maintenance activities, including dates, generator parts replaced, and any issues identified during inspections. This log provides a history of the generator maintenance.
8. Scheduled Professional Service
Depending on your generator's type and usage, schedule routine professional generator maintenance with a certified technician. They can perform more in-depth inspections and service tasks.
9. Generator Maintenance Kits
Keep a generator maintenance kit with spare parts and any critical components that may need replacement in a pinch. You can either gather these parts yourself individually or purchase a pre-assembled generator maintenance kit.
Should I Use a Generator Maintenance Kit?
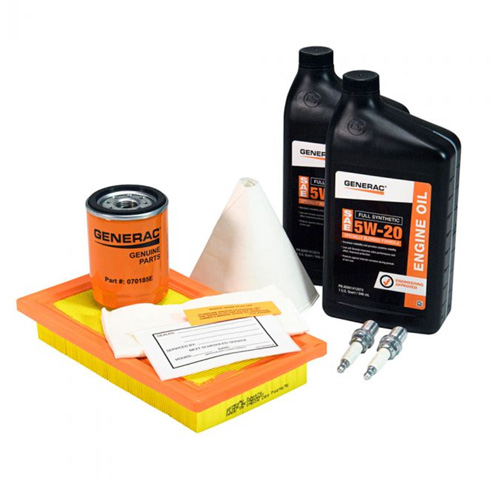 Generac generator maintenance kits are great for mechanics and do-it-yourselfers alike. The kits come with everything you need to perform routine generator maintenance on your generator, as well as how to make quick and easy repairs to keep your generator fully functional. Our kits come premade with all the basics, including proprietary replacement oil, air and oil filters, spark plugs, and shop towels. We also include easy-to-follow instructions to empower our customers to make the repairs themselves.
Generac generator maintenance kits are great for mechanics and do-it-yourselfers alike. The kits come with everything you need to perform routine generator maintenance on your generator, as well as how to make quick and easy repairs to keep your generator fully functional. Our kits come premade with all the basics, including proprietary replacement oil, air and oil filters, spark plugs, and shop towels. We also include easy-to-follow instructions to empower our customers to make the repairs themselves.
Generators are the unsung heroes of our modern world, providing power when and where we need it most. Understanding how a generator works is not only fascinating but also highlights the ingenuity and innovation that have shaped our electrified world. Whether it's a massive hydroelectric plant or a compact portable generator, the principles of converting mechanical energy into electrical power remain at the core of this vital technology.